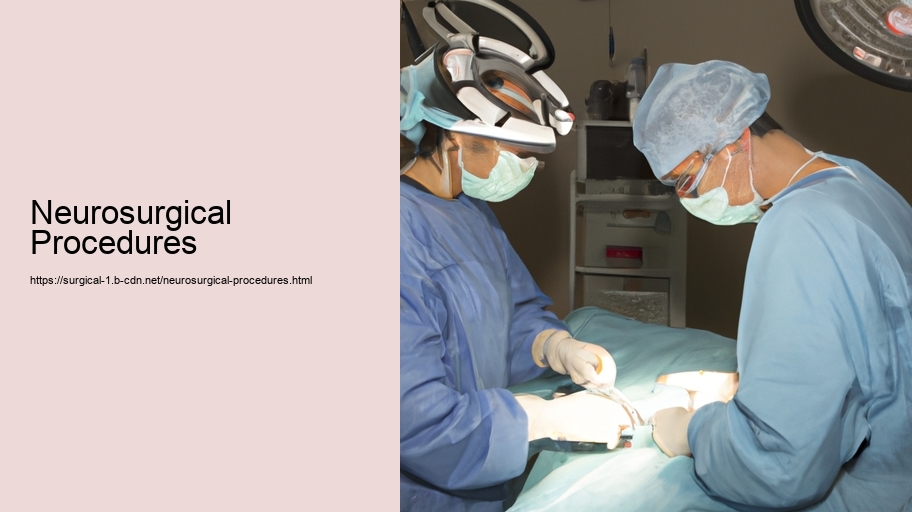
Neurosurgical procedures encompass a broad range of operations that are performed on the nervous system, particularly the brain and spinal cord. These intricate and delicate interventions are designed to treat disorders that affect the central and peripheral nervous systems, including congenital anomalies, trauma, tumors, vascular disorders, infections, degenerative diseases, and functional disorders.
The evolution of neurosurgery as a medical discipline has been marked by advancements in technology, surgical techniques, and an enhanced understanding of neuroanatomy and neurophysiology. From trephination, an ancient surgical practice of drilling holes in the skull, to contemporary microsurgery and stereotactic procedures, the journey of neurosurgical development reflects a relentless pursuit of improving patient outcomes and expanding the frontiers of what can be achieved through surgery.
One of the most common types of neurosurgical procedures is the removal of brain tumors. Brain tumors can be malignant or benign, but in either case, they may cause significant neurological impairment due to their size and location. The goal of neurosurgeons is to remove as much of the tumor as possible while preserving vital brain functions. This often involves the use of sophisticated imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, to plan the surgery and guide the surgeon during the operation. Intraoperative monitoring, which allows real-time assessment of the patient's brain function, has greatly increased the safety of these procedures.
Another area where neurosurgery has made significant strides is in the treatment of vascular disorders, such as aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). These conditions can lead to life-threatening hemorrhages or strokes if not managed properly. Through techniques like clipping for aneurysms or embolization for AVMs, neurosurgeons can prevent these catastrophic events. The introduction of endovascular neurosurgery, where surgeons can treat problems from within the vessels themselves, has revolutionized the field and offered less invasive options for patients.
Spinal surgery is another cornerstone of neurosurgery. Conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, fractures, and tumors can cause chronic pain and disability. Surgeons have a variety of tools at their disposal, including laminectomy, discectomy, and spinal fusion, to alleviate pain and restore function. Minimally invasive techniques have reduced recovery times and improved outcomes for many patients suffering from spinal disorders.
Functional neurosurgery is an intriguing sub-discipline that addresses conditions such as epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, and chronic pain. Procedures like deep brain stimulation (DBS) involve implanting electrodes in specific brain regions to modulate neural activity. This field is particularly exciting because it offers hope to patients with debilitating neurological conditions that are not amenable to medication or other forms of therapy.
Neurosurgical procedures are not without risks, and the decision to proceed with surgery is never taken lightly. The potential for complications, such as infection, bleeding, or neurological deficit, must be weighed against the potential benefits of the intervention. Surgeons, therefore, work closely with a multidisciplinary team, including neurologists, radiologists, and rehabilitation specialists, to provide comprehensive care for their patients.
In conclusion, neurosurgical procedures represent a pinnacle of medical achievement, combining technical skill with a profound understanding of the human nervous system. As research continues to unveil the mysteries of the brain and spine, and as technology advances, the field of neurosurgery holds the promise of even greater breakthroughs. The ultimate goal of these endeavors is to improve the quality of life for individuals afflicted with neurological conditions, offering them hope and the possibility of a brighter, healthier future.